Treating nasopharyngeal cancer in St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou
In St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou, we provide nasopharyngeal cancer patients with 18 advanced anticancer technologies and high quality services, and we will try our best to help them improve their living quality, relieve their pain and prolong their survival time. The MDT (Multidisciplinary Team) of St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou will make therapeutic plan for nasopharyngeal cancer patients based on their condition. Combining minimally invasive therapies with historic traditional Chinese medicine, nasopharyngeal cancer patients can avoid the suffering of traditional operation, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Meanwhile, experts will monitor the whole treatment, and adjust timely to improve the efficacy.
We can offer help if you are diagnosed with nasopharyngeal cancer. Online appointment or telephone appointment: 010 2066616. Contact us now.
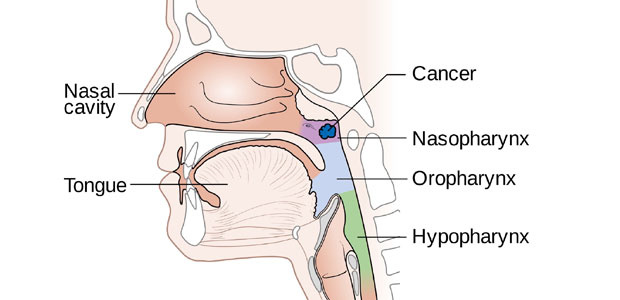
What is Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
The nasopharynx is the space situated behind the nose and below the brain. It connects the nose to the windpipe. On its sidewall, a tube connects it to the ear. Nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) develops when cells of the lining of the nasopharynx behave abnormally. A cancerous lump is formed which then invades out of the nasopharynx into the brain, ear and the jaw. It can spread to the lymph glands on one or both sides of the neck. It can also spread via the bloodstream to the lungs, liver and bones.
What are the Signs and Symptoms?
NPC often does not show any symptoms in the early stages.
Lump Its most common presentation (80%) is a painless lump in the neck. That is a swollen lymph node infiltrated by cancer cells.
Nose Bleeding, blocked nostrils, excessive mucus secretion, blood in saliva.
Ear Loss of hearing, pain, buzzing noise, discharge.
These symptoms may be due to other medical conditions. However, if they persist, consult a doctor.
Are You at Risk?
Diet Consumption of salted food such as vegetables, fish and meat is associated with NPC. Studies showed salted soy beans, canned pickled vegetables, szechuan vegetables and other salted vegetables are high risk food.
Epstein Barr Virus (EB virus)This virus has been found to be associated with NPC.
Genetic factors may play an important role in NPC. Blood tests can identify certain people at risk from NPC. Family history of Nasopharyngeal cancer increases the risks by four to ten-fold.
The Causes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer:
1. EB Virus is a lymphotropic DNA virus, which belongs to herpesviridae. It’s sporadic, but can cause a small epidemic, characterized by fever, skin rash, enlargements of lymph nodes, etc.
2. Environmental factor is also an important reason of nasopharyngeal cancer. Studies show that the Nickel content of nasopharyngeal cancer high prevalence is higher than that of nasopharyngeal low prevalence area. Animal studies show that Nickel can cause nasopharyngeal cancer.
3. Nasopharyngeal cancer is related to the race (the morbidity of the yellow is higher than that of the white) and genetic factor.
How to Prevent?
Eat plenty of fresh fruit, green vegetables and other sources of vitamin C to lower your cancer risk.
Avoid taking excessive amounts of salted fish and other preserved foodstuff.
Avoid active and secondary tobacco smoke exposure.
How is Nasopharyngeal Cancer Diagnosed?
The following tests are important:
Endoscopic examination A flexible fibre-optic tube with a light at its tip is introduced via the nose. The nasopharynx is examined visually and any suspicious lump is biopsied i.e. a small piece of the lump is removed and examined under the microscope.
CT scan of head and neck This is a special X-ray which can show the cancer and the extent of its spread. This test is also used in planning the treatment.
Blood test to determine the level of antibodies against EB virus. If the level of antibodies is high, a diagnosis of NPC is suspected.
Chest and abdominal CT scans, bone scans are performed to determine whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
MRI head and neck and PET-CT scan have been increasingly used as alternatives in replacement of CT scans.
How is Nasopharyngeal Cancer Treated?
Radiotherapy is the use of high energy x-rays to kill cancer cells. NPC responds well to radiotherapy, hence it is used as the main treatment for NPC. Radiotherapy is given on a daily basis for 6 weeks. Temporary side effects include redness of skin of the neck, reduced saliva production causing dryness of the mouth and throat, mouth ulcers, loss of sense of taste and appetite. The lymph nodes in the neck are also treated by radiotherapy. Newer radiotherapy technique called Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) are now in frequent use to reduce the late side effects of radiotherapy while maintaining a high chance of cancer control and cure. Late side effects include skin hardening, hearing impairment, reduced saliva production and reduced thyroid hormone levels.
Chemotherapy is the use of toxic drugs to kill cancer cells. Its role in NPC treatment is limited and is used in 2 situations:
1. Advanced NPC which had spread to bones, liver and lungs.
2. In combination with radiotherapy to improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Surgery The role of surgery is limited in NPC treatment because it is very difficult to remove an NPC without injuring vital neighboring organs. If NPC recurs in an area which had received radiotherapy before, surgery can be used to remove the recurrence.
What is the Outcome After Treatment?
Early stage: When the NPC is small and located only in the nasopharynx, the survival rate is very good (90%) after radiotherapy.
Intermediate stage: When the NPC has invaded the neighbouring organs or the lymph glands in the neck, the survival rate drops (50 to 75%).
Late stage: When the NPC has spread elsewhere in the body, the survival rate is poor (less than 10% of patients survived 5 years).






 Telephone:
Telephone: