What is cervical cancer?
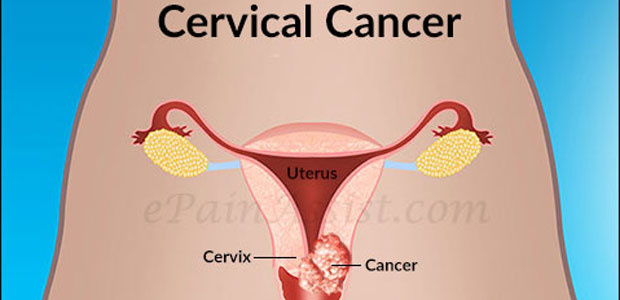
Female reproductive system consists of ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus (womb) and the vagina.
Cervix is the neck of the womb, which is visible during a vaginal examination. Cervix is made up of millions of tiny cells. Sometimes, some pathological changes can occur to these cells without you knowing it. These changes, if left untreated, could develop into cervical cancer. Among which, the infection of the cervix with human papilloma virus (HPV) is the most common cause of cervical cancer. These abnormal cells are called intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). If left untreated, they may slowly become cancerous.
What are the signs and symptoms of cervical cancer?
The main symptoms are:
Vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
Bad-smelling vaginal discharge
Irregular bleeding between periods or after menopause
Pre-cancerous and early stage of cervical cancer often comes without obvious symptoms. In this situation, cervical cancer is usually detected by routine vaginal examination and Pap smear.
Are you risky?
All women may have the risk of developing cervical cancer. Your risk increases if you are:
Sexually active;
Smoking;
Had multiple sexual partners;
Had a history of sexually transmitted infections, such as genital warts or genital herpes
How to prevent?
Reducing early sexual activity and the numbers of sexual partners;
To use condom during sexual intercourse as a form of protective measure;
To do regular Pap smear test;
Sexually active women above 25 years old are advised to have a Pap smear regularly. An initial smear is performed once a woman is sexually active and repeated after one year. After that, the Pap smear can be done once in one to three years as advised by the doctor.
How is cervical cancer diagnosed?
The following tests are important:
Pap smear: About 1 in 10 Pap smears will show some changes in the cervix, but if these changes are not indicative of cancer. Further tests will be needed to confirm the findings. If you are a virgin, you do not need to do the Pap smear. However, please consult a doctor immediately if there is any unusual bleeding.
Colposcopy: A colposcopy is an instrument use to examine the cervix with magnification.
Endocervical curettage: A method applied with passing an instrument into the cervix to obtain tissue for microscopic examination.
Cone biopsy: A large portion of the cervix is surgically removed for microscopic lab test. This procedure is performed under local anaesthesia.
How is cervical cancer treated?
Treatment differs from different stages:
Pre-cancerous stage: In this stage, the abnormal lesion area can be destroyed by using laser, diathermy (heat treatment) or cold coagulation (freezing the cells).
Cancer in situ (early stage cervical cancer): Removal of the womb (hysterectomy) may be used if a women who have had a child. However, many women may want to retain their wombs. In this condition, they might be suggested for cone biopsy or laser treatment.
Surgery is usually used to treat cancer that has not invaded beyond the cervix. The womb, fallopian tubes, ovaries, nearby tissue and lymph glands are also removed to ensure clearance of the cancer.
For cervical cancer that has invaded beyond the cervix, patients may be given other treatments based on their condition besides radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Those treatments in Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou can be interventional therapy, cryotherapy, immunotherapy, seed implantation, traditional Chinese medicine and so on.
The patient will be checked regularly after surgery, radiotherapy or other related treatments.
Sexual intercourse should be avoided temporarily after treatment.
Normal physical and social activities can be resumed in two to three months after treatment.






 Telephone:
Telephone: